Please check the status of this specification in Launchpad before editing it. If it is Approved, contact the Assignee or another knowledgeable person before making changes.
Launchpad Entry: Mobile-MediaPlayer
Packages affected:
Summary
The media viewer application for mobile devices. This is not the spec for the underlying engine (e.g. gstreamer, helix, etc). The media player for UME will have a finger-navigable UI capable of viewing photos, playing music and videos, and using either the gstreamer or helix media engines with a common interface to them. The UI will follow the recommendations in the UI Style Guide
Screenshots at the bottom
Rationale
There are some existing media applications but none seem to cover all of the features needed and be tailored for a MID, so a new UI is being written. The goal is to simplify the media management on the MID and provide a single place for viewing and listening to media.
Gstreamer and Helix media engines will be supported with dynamic discovery of the content types supported by whichever engine is present at runtime. Helix support is being included primarily for DRM solutions.
Use Cases
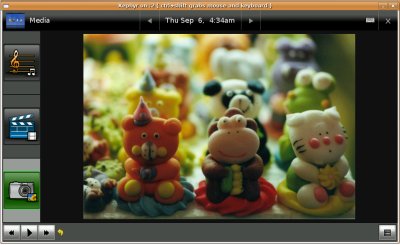
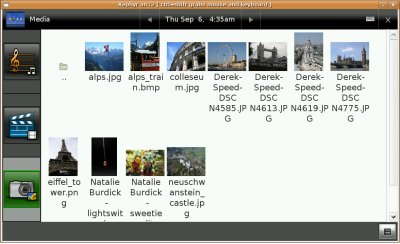
1. Photos. A user opens the media viewer and clicks on the "Photos" icon (currently a camera). The thumbnail view of all the photos in the top-level folder are displayed. The user can scroll through the thumbnails and touch one to see a bigger version. The user can click the "full screen" button to see the picture full screen.
1b. Photo organization (TBD). User can organize photos into folders using simplified file manager type UI.
2. Photo Slideshow. A user wants to create and view a slideshow of their pictures. By default, if the user is in a folder and clicks "Play" button, the pictures currently shown in the thumbnail view will start showing full screen as a slideshow starting with the one selected or the first one in the folder if none are selected. The user can create new slide shows by selecting the "New slideshow" option on the left (not currently implemented). User can assign one or more songs to play during the slideshow and also set the length of time between pictures.
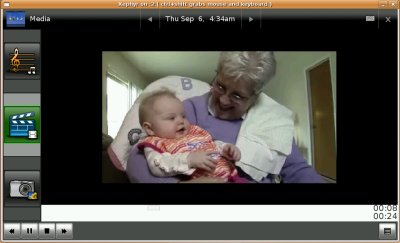
3. Video. A user opens media viewer and touches the "Video" icon (currently a director's scene tool). All of the videos in the top-level folder are displayed as thumbnails with a frame from the movie, or user-defined jpg image showing. User scrolls through thumbnails and picks desired video. User touches video and it begins to play in the area of the thumbnails. User can use the buttons at the bottom to control the play, pause, rwd, fwd. User can also click "Full Screen" to show the video playing fullscreen.
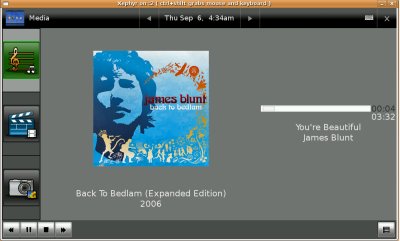
4. Music. A user opens media viewer and touches the "Music" icon (currently a treble clef and song notes icon). All music is displayed in an alphabeticallhy-organized list. User can change the way that music is viewed as list or albums. User can scroll through list and select the song they want. User touches the icon and the song starts to play. User can pause,play,fw,rwd the music using the buttons at the bottom of the screen. (Eventually visualizations could play when music plays).
4b. Music viewed as albums (TBD). User can select to view the music as albums. The thumbnail view to the right then shows albums in a row at the bottom and the list of songs in each album above in a list. User can touch albums and see songs, scroll through albums, etc. Albums may eventually be scrolled with fancy 3D effects.
5. Music Playlist (TBD). User can create a playlist of their favorite songs. User clicks "new playlist" button when in Music mode and adds songs to the playlist (not yet impl).
6. Internet Radio 6a. (manual) User clicks "Open URL" button at the bottom when in Music mode and can type in a URL. The user clicks "OK" and the media player connects to that URL attempts to play the streaming media assuming that codec support exists for it. 6b. (from browser). See #7.
7. Player content from web. User browses to content on a website using the web browser. User clicks the MP3, non-flash video, or streaming audio or video link. Media Viewer is launched and the media content is played by the Media Viewer. If user wants to continue browsing (while music plays) the user can toggle back over to the Web Browser and continue browsing without closing Media Viewer.
Scope
The entire scope of media management is large, from the first time a user obtains some content to consuming it on the device. The following section describes the full spectrum with the ones outside the scope of this application shown in red. Additional functionality may be added as time and resources permit.
Functional Specification
PC = non-mobile device, such as a Linux or Windows desktop
MID = Mobile Internet Device.
Content = music files (mp3, etc), movies (.mpg, etc), photos (.jpg, etc)
Media viewer = Multimedia application on MID
1. Content Management on the PC
(Currently not planned) There are a few choices for music management on the PC (e.g. Windows Media Player, ITunes, Banshee). For movie and photo management, users often use the filesystem directly. Eventually a new "MID Content Manager" application could be written.
2. Getting content to the device
- 2.1 Syncing
* Auto-sync with an application that manages content on the PC. This involves writing a new plugin or application that pushes the content from one of the following applications to the MID when the MID is plugged in via USB.
* Only sync down (all content is pushed to MID. Any MID content changes are lost
* Sync in both directions: content is merged on PC and MID. Conflicts are resolved by asking user for preference.
* Auto-sync with a file directory on the PC (just file system). Application registered when MID is plugged in to USB to auto-sync contents.
- Manual-sync: Plug MID into USB port. MID file system exposed to PC. User drags/drops files from PC to the MID file system.
* Auto-detect other MIDs in area via bluetooth. Connect. Display shared content from each MID on other MID. User can download content to their MID.
- Receive email with content. Save content to MID filesystem.
- On MID, download content from internet via the browser
- On MID, download/upload content from wired or wireless connection to remote filesystem over network
3. Content Management on MID
- User can:
- View content name, artist, album, length, genre, music format, times played, last played date/time
- View content as list
- View content as thumbnails (album art for music, cover-art for movies or frame from movie, small image for photos)
- View content as resizable thumbnails
- View 3D-flipping album art
- Select content
- Select multiple files at the same time
- Organize content folders, create new folders, name folders, move content between folders
* Assign content metadata: Name, Artist, Album, genre, cover art
* Auto-lookup music metadata online from CDDC: Name, artist, album, cover art
- Create, delete, edit playlists
- Sort music by: Name, Date, length, Artist, Album, genre, type (mp3, wav, etc)
Slideshow
- Create a slideshow of photos
- Assign a music file to play when slideshow is started
- Assign a music playlist to play when slideshow is started
- Set the time delay between photo transitions
- Set transition effect between pictures (fade, slide, etc)
4. Content Playback on MID
- User can:
- Play content
- Pause content
- Play content at double speed forward and backward
- Play content at variable speed forward and backward
- Jump to beginning of content
- Jump to end of content
- Stop content
- View progress of content playback
- View time content has been playing
- Jump to location within the content by moving the progress thumb to a new location
Video
- Play full screen video
- Pause and restart full screen video without leaving full screen Audio
- Show visualizations while playing audio
- Show visualizations full screen while playing audio
- Start audio and play it in the background while performing other tasks
- Easily pause audio that is playing in the background
Photo
- Show photos full screen.
- Navigate to next and previous photos
- Play slideshow
- Pause full screen slideshow and restart without leaving full screen
5. Internet Radio
- User can:
- Create, edit, and delete internet radio stations
- Select a station and listen to streaming audio
- Add a new internet radio station from inside the browser.
6. Content Plugins
- Media viewer will support mechanism for applications to register for certain content types and show buttons to launch these applications when the content of the registered type is selected. Plugin applications will be started with the paths to all the content as command-line parameters. Examples include internet upload, email, or any application to manipulate content.
7. Theme / Skin
- Media viewer will use the system theme for all standard Hildon and GTK controls such as buttons, scrollbars, and dialogs.
- User can change the skin of the MID media viewer
8. Media Engine
- Media viewer will be capable of using gstreamer or helix media playback engines
- User can select which media engine to use first, or exclusively
- Media viewer will dynamically discover what content types each media engine supports and attempt to playback content on the correct engine
- Media viewer will show a symbol on content that is not supported by any media engines
Design
Media Player is a D-Bus based multimedia player with media viewer and media engines. The D-Bus based Media viewer works as a client, and media engines work as servers. They interact by D-Bus interface for interprocess communication. Every media engine should provide a D-Bus object. Media viewer can call the members defined in D-Bus object, such as methods and signals.
Inside media viewer, there are engine management and music management. Engine management check and get all the engines in current system, get the capablities of engines, choose the right engine for a specific media content to be played. Music management can manage all the audio content in current system and show the audio content to users in playlist or album mode. Music management allow user to add/delete/rename the playlist, repeat/shuffle play content inside a playlist, and search/sort inside a playlist.
Implementation
The GUI is drawn by Glade Interface Designer. The media viewer and gstreamer D-Bus engine are written in python, so many python binding libraries are used in media player project, such as gtk, dbus, pygst, gobject, optparse, etc. A serial uniform of D-Bus interface has been defined, and all the media engines should follow this definition for their D-Bus interface.
Screenshots
Playing Music
View Photo
View Photo Thumbnails
Watch Video
Outstanding Issues
BoF agenda and discussion
UDS Media Player Issues/Suggestions
- navigation awkward
- thumbnail/fullscreen icons are not intuitive
- importing from USB card should be easier than traversing using a standard file manager
- smarter file import dialog that chooses approprite content from drive and only show you the applicable stuff
- usb input is contextual. photo mode only shows photo content on the usb drive
- pane on the left shows folders or icons and right side shows content
- preference for showing photo titles so you can turn it off
- show list view or thumbnail view for videos, photos and music
- list view should be sortable
- allow editing of metadata for all content types
- Support for albums, folders, or some other organization metaphor in the ui
- allow slideshows of an album
- single level of folders is probably enough for most use cases
- How to integrate videos in with photos? IPhoto/Picassa show video thumbnails. Do we do this or just show the videos in the video section?
- Large icons on left (movies, photos, music) take up a lot of space with little utility
Maybe just make them smaller? <- refer to the UI guide
- Gesture support: currently have back/next support
- rotate gesture desirable
- zooming gesture desirable
cropping and redeye interface for pluggin in tools <- That should go into the camera applications <- but, these features would also be useful for photos imported from an external camera
- Metadata questions: whether to directly edit the source files or create seperate files that contain metadata. Perfomarnce issues might dictate using serparate file
- Possible optimizations to speed the UI
- Getting metadata out of large files takes time (and photo files get larger all the time)
- Can keep a cache of thumbnails and smaller versions of photo at resolution optimized for screen
- Saving and Exporting Photos:
- from cheese, when you save a photo it should automatically put it in the Media Library
- need a way to export photos, email photos of particular interest. This can be accomplished by writing a Media player plugin
- Videos subtitle support desirable
- Translucent on-screen transport controls desireable
- Generating video thumbnails might only want to done on import, not just in the background as this might negativley impact performance.
- Music - get the cover art feature would be nice
App title in marquee should be something other than "MoblinMedia.py"
- Need to be able to organize by artist, album, genre, playlist
- Need search capability for above category (or some sort of smart filtering ala iPhone)
- track number metadata needs to be included
- Performance issues need to be investigated: it is slow even with no content
- Investigate how metadata is retrieved when importing songs. Could be a big performance hit if it's going across dbus. Need to figure out how the metadata retrieval is happening
- Have consistent UI for zooming like it is currently implemented in Media Player. Can this be standard across all UME apps? Would be nice.
Why not just use XBMC as the framework base for this mobile media player? XBMC practically have all of the features wanted already, and it was originally designed to run on an embedded-system so it is small and memory efficient, plus it has a VERY flexible skinning and GUI engine to you could make the skin/theme and navigation look and act like anything you want, windowed or full-screen. It is open source (GPL) and runs on Ubuntu Linux with not too many dependecies, the only real downside I see with it is that the Linux version of XBMC is in pre-alpha stage however it is never the less still very usable 'as is' right now. Checkout the XBMC Linux port project article (or just get a good overview of XBMC by reading the Wikipedia article).